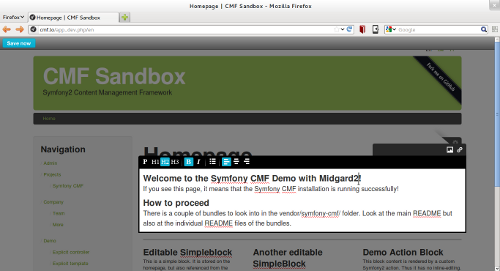
Running Symfony CMF with Midgard2
I’ve written about Decoupled Content Management before. As the Symfony Live event in Paris is nearing, I thought to give Symfony CMF a spin. Symfony CMF is a new approach at building PHP content management systems, and adheres quite well to the principles of decoupled CMS:
- Content is stored into a standard PHP Content Repository
- Symfony2 is used as the web framework
- Front-end editing works on the Create.js stack of VIE and Hallo
I’m especially happy with the front-end editor, which has been implemented by Liip as part of their IKS Early Adopter project.
Most developers working on Symfony CMF have focused on using the Apache Jackrabbit PHPCR backend, but as you’ll see in this tutorial, it works just fine also using the Midgard2 PHPCR provider. The advantage of using Midgard2 is a simpler stack, as you don’t need any external Java processes and all data access happens with typical RDBMSs like MySQL and Postgres using a simple PHP extension.
Being able to run the same CMS with two completely different content repository back-ends is truly a sign of proper decoupling.
Getting started
First of all you need a Symfony2 application that uses the Symfony CMF bundles. Since not many of these are around yet, the best way to start is by installing the CMF Sandbox demo.
You can get this with a Git checkout:
$ git clone https://github.com/symfony-cmf/cmf-sandbox.git
Dependencies
To use Symfony CMF with Midgard2, you obviously need the PHP extension installed. Midgard2 is available in new Ubuntu and Debian releases, and so most likely the installation is as simple as:
$ sudo apt-get install php5-midgard2
For those on Mac OS X, the Midgard2 extension is also available on MacPorts.
The Midgard2 PHPCR provider also uses some necessary content schemas. Grab these two files:
and place them in /usr/share/midgard2/schema.
Configuring Symfony CMF to use Midgard2
Copy the app/config/parameters.yml.dist file to app/config/parameters.yml and edit it. Depending on what database you’re using with Midgard2, the configuration could look something like:
parameters:
locale: en
secret: xxxxxxxxxx
phpcr_backend:
type: midgard2
db_type: SQLite
db_name: cmf
db_dir: /tmp
db_init: true
blobdir: /tmp/cmf-blobs
loglevel: warn
phpcr_workspace: default
phpcr_user: admin
phpcr_pass: password
With a MySQL database, the db_* parameters would be something like:
phpcr_backend:
type: midgard2
db_type: MySQL
db_name: midgard2
db_username: root
db_password: password
Installing with Composer
All PHP-level dependencies of Symfony CMF are installed with Composer. Download it with:
$ cd cmf-sandbox
$ wget http://getcomposer.org/composer.phar
Jackrabbit is the default PHPCR implementation in Symfony CMF. To get Midgard2 PHPCR provider also installed, run your Composer installation with:
$ php composer.phar update --dev
Preparing the database
Symfony CMF requires some additional PHPCR data to be loaded. Handle that with:
$ app/console doctrine:phpcr:register-system-node-types
Then you can load some initial content to your Sandbox site:
$ app/console -v doctrine:phpcr:fixtures:load
Now your Midgard2 CMF database is ready! Edit your app/config/parameters.yml and change the dbinit parameter to false. This is important because otherwise Midgard2 perform a number of database structure checks every time it is loaded.
Using Symfony CMF
Once all of this is done and you have a working Symfony2 server setup (I’m running it with nginx), you should be ready to start using the CMF.
The site can be found under the /app_dev.php/ path of your server, so for example on my system it is in http://cmf.lo/app_dev.php/en.